
Portland Bolt manufactures a wide range of bolts and fasteners to numerous standards set by many different organizations and specifying committees. There are many different organizations for fasteners, all of which have their own set of standards and guidelines for manufacturing. We, as estimators, are often asked what the acronyms for such organizations and committees stand for. Here is a detailed list with explanations for each of these organizations and committees.

ASTM International (Formerly American Society for Testing and Materials)
ASTM International is a globally recognized leader for developing international standards. Currently, there are at least 12,000 ASTM standards that are used throughout the world. These standards are used to improve product quality and enhance safety in the products consumers are purchasing. There are more than 30,000 members of the world’s top technical experts and business professionals, from 150 countries, currently contributing to ASTM’s development. Portland Bolt employees, Dane McKinnon and Gary Rusynyk, are voting members on Committee F16 that oversees fastener specifications.
ASTM specifications provide crucial manufacturing information for fasteners. These specifications outline the chemical and mechanical properties that the bolt must conform to in order to meet the specification. The requirements also include, but are not limited to: testing, strength and marking requirements.

SAE International (Formerly Society of Automotive Engineers)
SAE is a U.S. based, global association of more than 138,000 engineers and technical experts with a primary focus in the aerospace, automotive, and commercial-vehicle industries. The SAE core proficiencies are life-long learning, and voluntary consensus standards development.
The primary SAE specification for fasteners is J429; which includes Grades 2, 5 and 8 bolts. Another common SAE specification is J995 for steel nuts. These specifications provide mechanical and material requirements for the fasteners and/or nuts used in automotive and other related industries.
 AASHTO: American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials
AASHTO: American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials
This standards organization publishes test protocols, specifications and guidelines which are used in highway design and construction through the U.S. AASHTO not only represents highways, it also represents air, rail, water and public transportation systems. The primary goal of this association is the further development, operation and maintenance of the national transportation systems.
Many state transportation projects call out AASHTO designations for their bolts. This AASHTO specification often translates directly to an ASTM specification. This ASTM to AASHTO Conversion Table shows the direct correlation from AASHTO to ASTM specifications. Portland Bolt is an approved supplier for 100% domestic highway fasteners for State Departments of Transportation throughout the U.S. We manufacture products to AASHTO specifications on a daily basis.
 AISI: American Iron and Steel Institute
AISI: American Iron and Steel Institute
The AISI is an association of North American steel producers. It has been in existence for over a century, making it the oldest trade association in the U.S. This organization advocates for public policies that support competitive domestic manufacturing while providing high-quality products to a wide range of customers. One of the goals of the AISI is to increase the market for North American Steel in both traditional and innovative applications.
This organization is attempting to make steel the primary choice of material used in a variety of applications, fasteners being one of them. They provide information on many types of steels used throughout the fastener industry which furthers the understanding of each type of steel that can be used as a high performance product. This helps advance the use of steel in the current competitive marketplace.
 ANSI: American National Standards Institute
ANSI: American National Standards Institute
This institution is known as the voice of the U.S. standards and conformity assessment system. They oversee the creation, promulgation, and use of thousands of guidelines that directly impact business in nearly every sector. They have guidelines ranging anywhere from acoustical devices to construction equipment, and from dairy and livestock production to energy distribution. They also are active in accreditation programs that assess conformance standards and management systems.
 ASME: American Society of Mechanical Engineers
ASME: American Society of Mechanical Engineers
This non-profit organization enables the collaboration, career enrichment, and skills development across all engineering disciplines toward a goal of helping the global engineering community develop solutions to benefit lives and livelihoods. Founded in 1880, this organization has grown to now include more than 130,000 members in 158 countries. ASME serves a wide range of quality programs, including codes, standards and publications.
ASME standards provide manufacturers with guidelines and tolerances that their bolts must conform to. Some types of bolts, such as hex cap screws used in the automotive industry, require very tight tolerances, whereas other construction grade fasteners have looser tolerances. All of these tolerances are defined by the specifications in the ASME and are crucial for the manufacturing process.
 IFI: Industrial Fasteners Institute
IFI: Industrial Fasteners Institute
The IFI is an Ohio-based trade and standards organization and publisher. Established in 1931, the primary focus of the IFI is to represent the interests of North American mechanical fastener manufactures. Their standards are frequently used as a design guide by mechanical engineers, machinists, and other manufacturers of machine screws, bolts, nuts, and other engineered fasteners.
In regard to fasteners, the IFI does not create their own standards but they do manage fastener standards. They are responsible for creating technical information and writings which are featured in their IFI handbook, but their main function is to support, protect and represent fastener manufacturers.
 CSA: Canadian Standards Association
CSA: Canadian Standards Association
CSA is a standards development organization that was established in 1919. They are accredited to develop standards in both Canada and the United States. Since their beginnings in 1919, the CSA group has grown to be the largest standards development organization in Canada. They also hold the largest subject area recognition. Currently, their library consists of over 3,000 standards and codes. The standards that affect the fastener industry provide chemical and mechanical properties for the manufacturing process.
The most common steel specification from the CSA is G40.21. This specification covers the mechanical and chemical requirements for structural steel shapes, plates and bars for use in general construction and engineering. The most common grade of G40.21 is 44W (300W). Most steel mills in the US manufacture their round and flat bar to meet this grade and ASTM A36 so that both countries’ requirements may be satisfied. Another grade, 50W, has become more common in recent years. This grade is similar to the ASTM specification A572 Grade 50. All of Portland Bolt’s A36 round bar will cross-certify to meet the Grade 44W requirements and our Grade 55 round bar will meet the Grade 50W requirements.
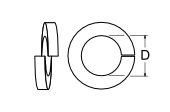
 The term “lock washer” can include a huge variety of different products used in many different applications that often are very specific and can include many different grades, materials and purposes. When our customers refer to a lock washer, we assume they are referencing a “split lock washer” that is a generic lock washer that you would see on any general construction site. Generic split Lock washers are not regarded as structural components, since they are just fixing a nut into place, and thus do not have the same amount of scrutiny that nuts and bolts have. Due to this, there is currently no ASTM specification that covers a generic split lock washer. Also, there is no high strength lock washer specification by ASTM and generic lock washers are often used with high strength bolts, since there is no “high strength” lock washer specification or any grades at all for that matter.
The term “lock washer” can include a huge variety of different products used in many different applications that often are very specific and can include many different grades, materials and purposes. When our customers refer to a lock washer, we assume they are referencing a “split lock washer” that is a generic lock washer that you would see on any general construction site. Generic split Lock washers are not regarded as structural components, since they are just fixing a nut into place, and thus do not have the same amount of scrutiny that nuts and bolts have. Due to this, there is currently no ASTM specification that covers a generic split lock washer. Also, there is no high strength lock washer specification by ASTM and generic lock washers are often used with high strength bolts, since there is no “high strength” lock washer specification or any grades at all for that matter.


 ANSI: American National Standards Institute
ANSI: American National Standards Institute ASME: American Society of Mechanical Engineers
ASME: American Society of Mechanical Engineers IFI: Industrial Fasteners Institute
IFI: Industrial Fasteners Institute CSA: Canadian Standards Association
CSA: Canadian Standards Association There are many grades of
There are many grades of 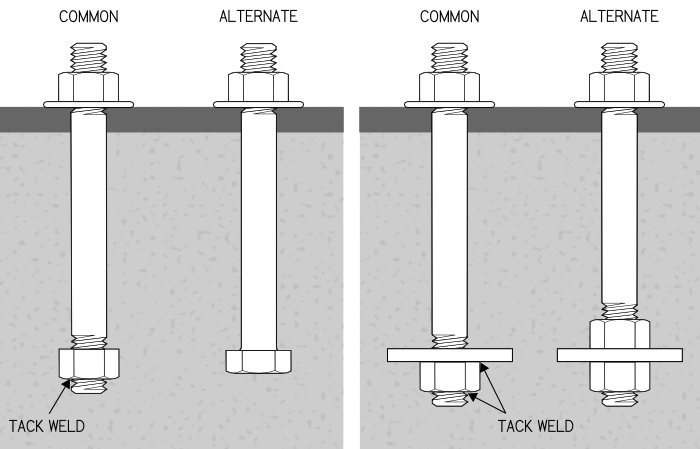

 The “X” designates the connection type (bearing-type connection with threads excluded from the shear plane) and has nothing to do with the bolt itself. Therefore, an A325 structural bolt used in this type of connection will have no different markings than an A325 bolt used in a different type of connection (N or SC). All A325 type 1 bolts are simply marked with “A325” and the manufacturer’s logo. The exceptions are as follows:
The “X” designates the connection type (bearing-type connection with threads excluded from the shear plane) and has nothing to do with the bolt itself. Therefore, an A325 structural bolt used in this type of connection will have no different markings than an A325 bolt used in a different type of connection (N or SC). All A325 type 1 bolts are simply marked with “A325” and the manufacturer’s logo. The exceptions are as follows:


 The simple answer here is no. ASTM A709 is a specification that covers carbon and high-strength structural steel plates and bars intended for use in bridge applications. There are multiple grades of A709 and Grade 36 covers the structural steel made from mild carbon steel, such as
The simple answer here is no. ASTM A709 is a specification that covers carbon and high-strength structural steel plates and bars intended for use in bridge applications. There are multiple grades of A709 and Grade 36 covers the structural steel made from mild carbon steel, such as